Spring Boot Constructor Injection Example
In this tutorial, we will learn how to use constructor-based dependency injection in the Spring boot application.
Dependency Injection is a design pattern on which dependency of the object is injected by the framework rather than created by the Object itself - It is also called IOC (Inversion of Control).
Dependency Injection reduces coupling between multiple objects as its dynamically injected by the framework. Spring IoC Container uses DI to inject one object into another object.
There are mainly three types of Dependency Injection:
In this tutorial, we will see step by step how to use constructor-based dependency injection in the Spring boot application.
Constructor Injection
Constructor injection uses the constructor to inject dependency on any Spring-managed bean.
Well, the Spring IOC container uses a constructor to inject dependency on any Spring-managed bean.
Constructor Injection Example
In order to demonstrate the usage of constructor injection, let's create a few interfaces and classes.
MessageService
public interface MessageService {
void sendMessage(String message);
}
EmailService
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class EmailService implements MessageService{
@Override
public void sendMessage(String message){
System.out.println(message);
}
}
We have annotated EmailService class with @Component
annotation so the Spring container automatically creates a Spring bean and manages its life cycle.
SMSService
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("smsService")
public class SMSService implements MessageService{
@Override
public void sendMessage(String message){
System.out.println(message);
}
}
We have annotated SMSService class with @Component annotation
so the Spring container automatically creates a Spring bean and manages its life cycle.
MessageSender
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageSender {
private MessageService messageService;
@Autowired
public MessageSender(@Qualifier("emailService") MessageService messageService){
this.messageService = messageService;
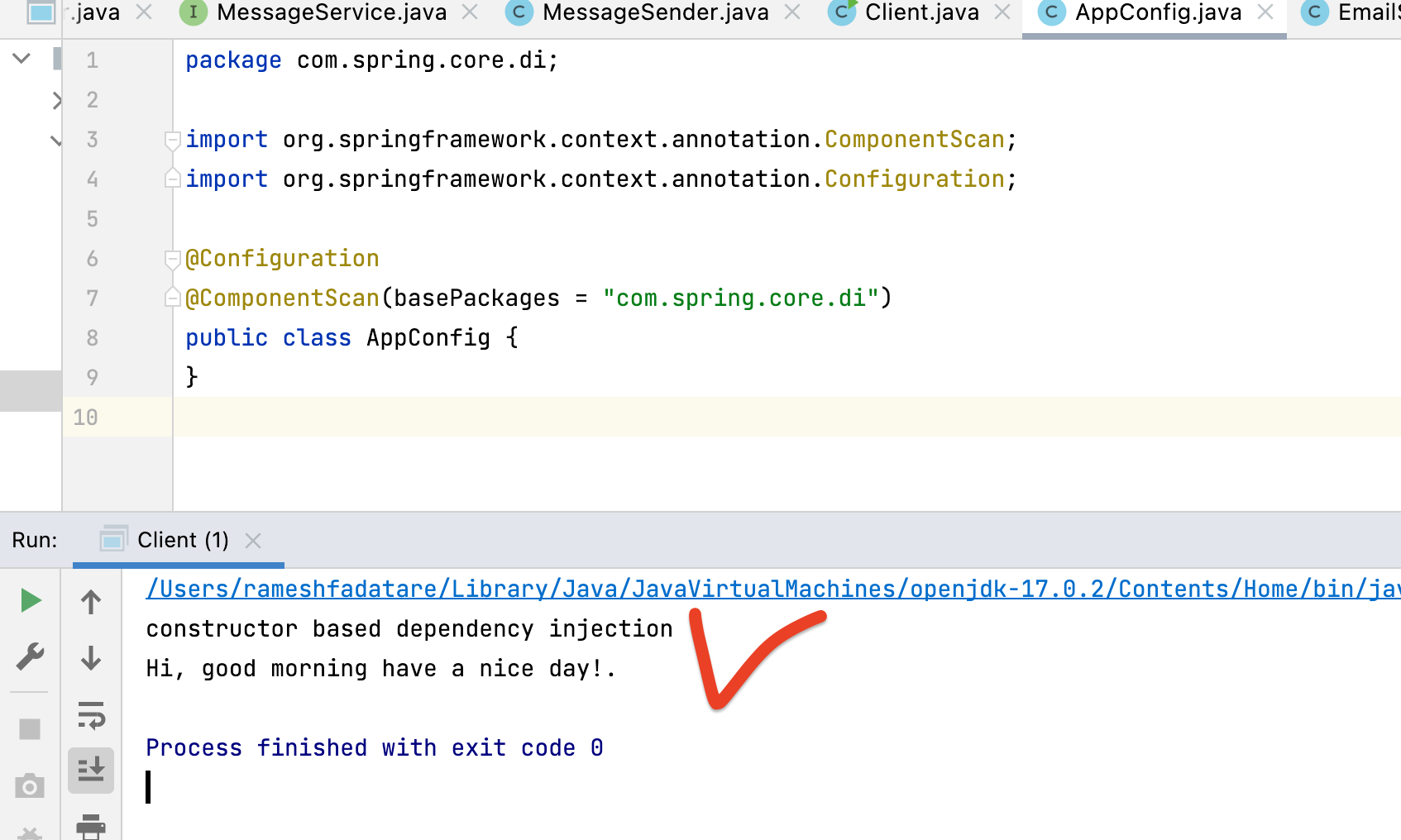
System.out.println("constructor based dependency injection");
}
public void sendMessage(String message){
this.messageService.sendMessage(message);
}
}
@Qualifier annotation is used in conjunction with Autowired to avoid confusion when we have two or more beans configured for the same type.
Spring @Autowired annotation is used for the automatic injection of beans.
Spring container uses the below constructor to inject dependency on any Spring-managed bean (MessageSender is a Spring bean):
@Autowired
public MessageSender(@Qualifier("emailService") MessageService messageService){
this.messageService = messageService;
System.out.println("constructor based dependency injection");
}
AppConfig
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.spring.core.di")
public class AppConfig {
}
@Configuration: to indicate that a configuration class declares one or more @Bean methods. These classes are processed by the Spring container to generate bean definitions and service requests for those beans at runtime.
@ComponentScan: This annotation is used to specify the base packages to scan for spring beans/components.
Testing
Let's create ApplicationContext and test this example:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
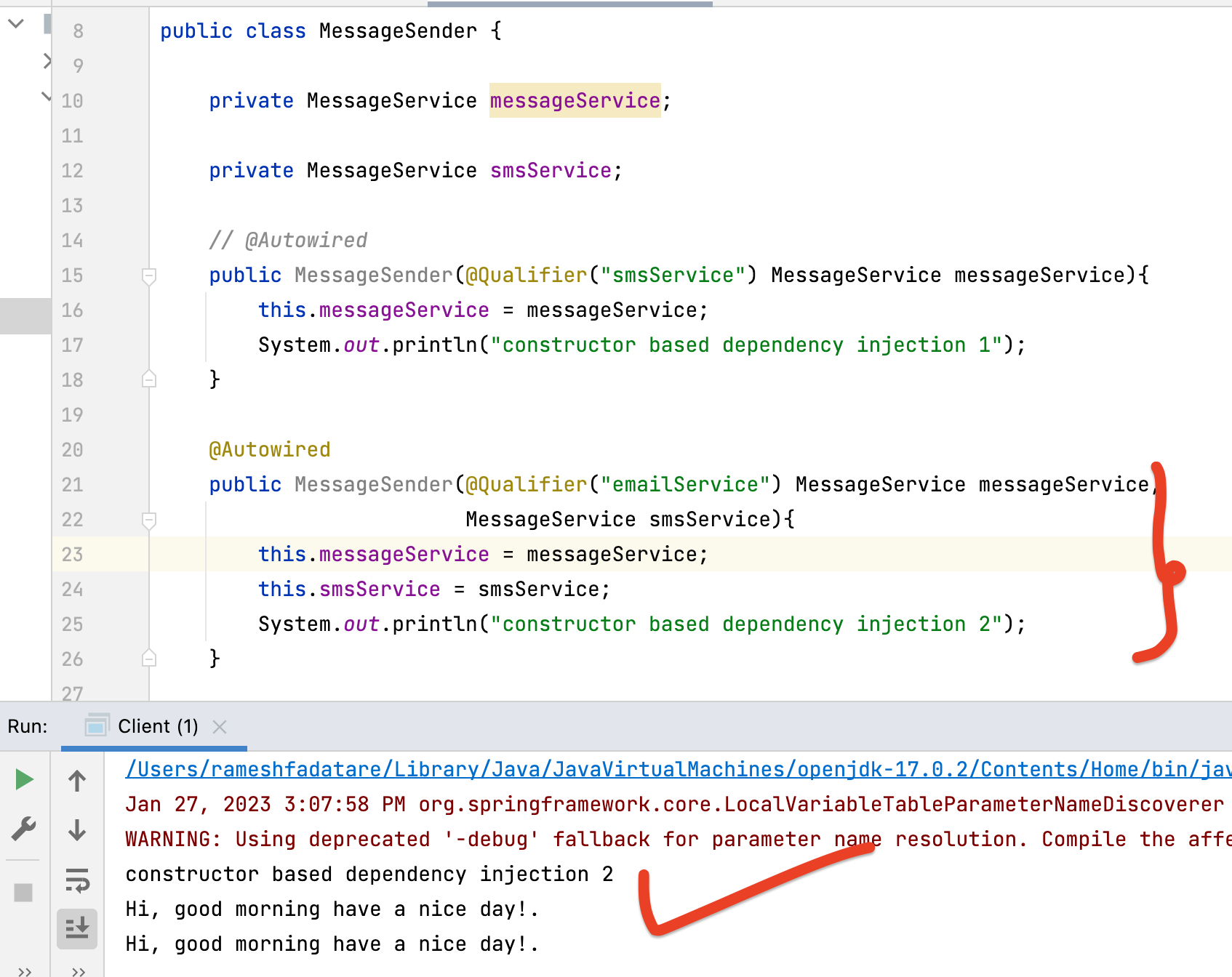
String message = "Hi, good morning have a nice day!.";
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MessageSender messageSender = applicationContext.getBean(MessageSender.class);
messageSender.sendMessage(message);
}
}
Output:
Update on @Autowired Annotation
Before Spring 4.3, we had to add an @Autowired annotation to the constructor. With newer versions, this is optional if the class has only one constructor.
When we have a class with multiple constructors, we need to explicitly add the @Autowired annotation to any one of the constructors so that Spring knows which constructor to use to inject the dependencies.
Example
In the below example, the MessageSender class has multiple constructors, so we need to explicitly add the @Autowired annotation to any one of the constructors so that Spring knows which constructor to use to inject the dependencies.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MessageSender {
private MessageService messageService;
private MessageService smsService;
// @Autowired
public MessageSender(@Qualifier("smsService") MessageService messageService){
this.messageService = messageService;
System.out.println("constructor based dependency injection 1");
}
@Autowired
public MessageSender(@Qualifier("emailService") MessageService messageService,
MessageService smsService){
this.messageService = messageService;
this.smsService = smsService;
System.out.println("constructor based dependency injection 2");
}
public void sendMessage(String message){
this.messageService.sendMessage(message);
this.smsService.sendMessage(message);
}
}
Output:
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we saw how to use constructor-based dependency injection in the Spring boot application. In the next tutorial, learn about Using Setter Injection in Spring Boot Application.