Spring Boot Integration Testing CRUD REST API with MySQL Database
In this tutorial, we will learn how to perform Integration testing Spring boot application using @SpringBootTest annotation.
Let's first take a look at the overview of @SpringBootTest annotation.
@SpringBootTest Annotation
Spring Boot provides @SpringBootTest annotation for Integration testing. This annotation creates an application context and loads the full application context.
@SpringBootTest will bootstrap the full application context, which means we can @Autowire any bean that's picked up by component scanning into our test.
It starts the embedded server, creates a web environment, and then enables @Test methods to do integration testing.
By default, @SpringBootTest does not start a server. We need to add the attribute webEnvironment to further refine how your tests run. It has several options:
- MOCK(Default): Loads a web ApplicationContext and provides a mock web environment.
- RANDOM_PORT: Loads a WebServerApplicationContext and provides a real web environment. The embedded server is started and listened to a random port. This is the one that should be used for the integration test.
- DEFINED_PORT: Loads a WebServerApplicationContext and provides a real web environment. NONE: Loads an ApplicationContext by using SpringApplication but does not provide any web environment.
Tools and technologies used
- Java 11+
- Spring Boot
- Spring Data JPA
- MySQL
- Lombok
- JUnit 5 Framework
- IntelliJ IDEA
- Docker
- Maven
What is Integration Testing
As the name suggests, integration tests focus on integrating different layers of the application. That also means no mocking is involved.
Basically, we write integration tests for testing a feature that may involve interaction with multiple components.
Examples: Integration testing of complete Employee Management Feature ( EmployeeRepository, EmployeeService, EmployeeController).
Integration testing of complete User Management Feature (UserController, UserService, and UserRepository).
Integration testing of complete Login Feature (LoginRespository, LoginController, Login Service), etc
1. Create Spring Boot Application
Using spring initialize, create a Spring Boot project and add the following dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Data JPA
- Lombok
- MySQL Driver
Generate the Spring boot project as a zip file, extract it, and import it into IntelliJ IDEA.
2. Configure MySQL database
Let's use the MySQL database to store and retrieve the data in this example and we gonna use Hibernate properties to create and drop tables.
Open the application.properties file and add the following configuration to it:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Mysql@123
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = create-drop
Make sure that you will create a demo database before running the Spring boot application.
Also, change the MySQL username and password as per your MySQL installation on your machine.
3. Create JPA Entity
Next, let's create an Employee JPA entity with the following content:
import lombok.*;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Setter
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Builder
@Entity
@Table(name = "employees")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private long id;
@Column(name = "first_name", nullable = false)
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name", nullable = false)
private String lastName;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String email;
}
Note that we are using Lombok annotations to reduce the boilerplate code.
@Entity annotation is used to mark the class as a persistent Java class.
@Table annotation is used to provide the details of the table that this entity will be mapped to.
@Id annotation is used to define the primary key.
@GeneratedValue annotation is used to define the primary key generation strategy. In the above case, we have declared the primary key to be an Auto Increment field.
@Column annotation is used to define the properties of the column that will be mapped to the annotated field. You can define several properties like name, length, nullable, updateable, etc.
4. Create Repository Layer
Let's create EmployeeRepository which extends the JpaRepository interface:
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface EmployeeRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Long> {
}
5. Create Service Layer
EmployeeService
Let's create an EmployeeService interface with CRUD methods:
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface EmployeeService {
Employee saveEmployee(Employee employee);
List<Employee> getAllEmployees();
Optional<Employee> getEmployeeById(long id);
Employee updateEmployee(Employee updatedEmployee);
void deleteEmployee(long id);
}
EmployeeServiceImpl
Let's create an EmployeeServiceImpl class that implements the EmployeeService interface:
import net.javaguides.springboot.exception.ResourceNotFoundException;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.EmployeeRepository;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl implements EmployeeService {
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
public EmployeeServiceImpl(EmployeeRepository employeeRepository) {
this.employeeRepository = employeeRepository;
}
@Override
public Employee saveEmployee(Employee employee) {
Optional<Employee> savedEmployee = employeeRepository.findByEmail(employee.getEmail());
if(savedEmployee.isPresent()){
throw new ResourceNotFoundException("Employee already exist with given email:" + employee.getEmail());
}
return employeeRepository.save(employee);
}
@Override
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
return employeeRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Optional<Employee> getEmployeeById(long id) {
return employeeRepository.findById(id);
}
@Override
public Employee updateEmployee(Employee updatedEmployee) {
return employeeRepository.save(updatedEmployee);
}
@Override
public void deleteEmployee(long id) {
employeeRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
6. Controller Layer
Let's create CRUD REST APIs for creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting an Employee:
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/employees")
public class EmployeeController {
private EmployeeService employeeService;
public EmployeeController(EmployeeService employeeService) {
this.employeeService = employeeService;
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public Employee createEmployee(@RequestBody Employee employee){
return employeeService.saveEmployee(employee);
}
@GetMapping
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees(){
return employeeService.getAllEmployees();
}
@GetMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> getEmployeeById(@PathVariable("id") long employeeId){
return employeeService.getEmployeeById(employeeId)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.orElseGet(() -> ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
@PutMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Employee> updateEmployee(@PathVariable("id") long employeeId,
@RequestBody Employee employee){
return employeeService.getEmployeeById(employeeId)
.map(savedEmployee -> {
savedEmployee.setFirstName(employee.getFirstName());
savedEmployee.setLastName(employee.getLastName());
savedEmployee.setEmail(employee.getEmail());
Employee updatedEmployee = employeeService.updateEmployee(savedEmployee);
return new ResponseEntity<>(updatedEmployee, HttpStatus.OK);
})
.orElseGet(() -> ResponseEntity.notFound().build());
}
@DeleteMapping("{id}")
public ResponseEntity<String> deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("id") long employeeId){
employeeService.deleteEmployee(employeeId);
return new ResponseEntity<String>("Employee deleted successfully!.", HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
7. Writing Integration Tests for CRUD REST API's
Now, let's create Integration JUnit tests for CRUD REST APIs. We gonna use the @SpringBootTest annotation to run Integration tests with respect to the MySQL database.
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import net.javaguides.springboot.model.Employee;
import net.javaguides.springboot.repository.EmployeeRepository;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.ResultActions;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import static org.hamcrest.CoreMatchers.is;
import static org.mockito.ArgumentMatchers.any;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.given;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.willDoNothing;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class EmployeeControllerITests {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@BeforeEach
void setup(){
employeeRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void givenEmployeeObject_whenCreateEmployee_thenReturnSavedEmployee() throws Exception{
// given - precondition or setup
Employee employee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("Fadatare")
.email("ramesh@gmail.com")
.build();
// when - action or behaviour that we are going test
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(post("/api/employees")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(employee)));
// then - verify the result or output using assert statements
response.andDo(print()).
andExpect(status().isCreated())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName",
is(employee.getFirstName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.lastName",
is(employee.getLastName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email",
is(employee.getEmail())));
}
// JUnit test for Get All employees REST API
@Test
public void givenListOfEmployees_whenGetAllEmployees_thenReturnEmployeesList() throws Exception{
// given - precondition or setup
List<Employee> listOfEmployees = new ArrayList<>();
listOfEmployees.add(Employee.builder().firstName("Ramesh").lastName("Fadatare").email("ramesh@gmail.com").build());
listOfEmployees.add(Employee.builder().firstName("Tony").lastName("Stark").email("tony@gmail.com").build());
employeeRepository.saveAll(listOfEmployees);
// when - action or the behaviour that we are going test
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(get("/api/employees"));
// then - verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.size()",
is(listOfEmployees.size())));
}
// positive scenario - valid employee id
// JUnit test for GET employee by id REST API
@Test
public void givenEmployeeId_whenGetEmployeeById_thenReturnEmployeeObject() throws Exception{
// given - precondition or setup
Employee employee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("Fadatare")
.email("ramesh@gmail.com")
.build();
employeeRepository.save(employee);
// when - action or the behaviour that we are going test
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(get("/api/employees/{id}", employee.getId()));
// then - verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName", is(employee.getFirstName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.lastName", is(employee.getLastName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email", is(employee.getEmail())));
}
// negative scenario - valid employee id
// JUnit test for GET employee by id REST API
@Test
public void givenInvalidEmployeeId_whenGetEmployeeById_thenReturnEmpty() throws Exception{
// given - precondition or setup
long employeeId = 1L;
Employee employee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("Fadatare")
.email("ramesh@gmail.com")
.build();
employeeRepository.save(employee);
// when - action or the behaviour that we are going test
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(get("/api/employees/{id}", employeeId));
// then - verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isNotFound())
.andDo(print());
}
// JUnit test for update employee REST API - positive scenario
@Test
public void givenUpdatedEmployee_whenUpdateEmployee_thenReturnUpdateEmployeeObject() throws Exception{
// given - precondition or setup
Employee savedEmployee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("Fadatare")
.email("ramesh@gmail.com")
.build();
employeeRepository.save(savedEmployee);
Employee updatedEmployee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ram")
.lastName("Jadhav")
.email("ram@gmail.com")
.build();
// when - action or the behaviour that we are going test
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(put("/api/employees/{id}", savedEmployee.getId())
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(updatedEmployee)));
// then - verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName", is(updatedEmployee.getFirstName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.lastName", is(updatedEmployee.getLastName())))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email", is(updatedEmployee.getEmail())));
}
// JUnit test for update employee REST API - negative scenario
@Test
public void givenUpdatedEmployee_whenUpdateEmployee_thenReturn404() throws Exception{
// given - precondition or setup
long employeeId = 1L;
Employee savedEmployee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("Fadatare")
.email("ramesh@gmail.com")
.build();
employeeRepository.save(savedEmployee);
Employee updatedEmployee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ram")
.lastName("Jadhav")
.email("ram@gmail.com")
.build();
// when - action or the behaviour that we are going test
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(put("/api/employees/{id}", employeeId)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(updatedEmployee)));
// then - verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isNotFound())
.andDo(print());
}
// JUnit test for delete employee REST API
@Test
public void givenEmployeeId_whenDeleteEmployee_thenReturn200() throws Exception{
// given - precondition or setup
Employee savedEmployee = Employee.builder()
.firstName("Ramesh")
.lastName("Fadatare")
.email("ramesh@gmail.com")
.build();
employeeRepository.save(savedEmployee);
// when - action or the behaviour that we are going test
ResultActions response = mockMvc.perform(delete("/api/employees/{id}", savedEmployee.getId()));
// then - verify the output
response.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andDo(print());
}
}
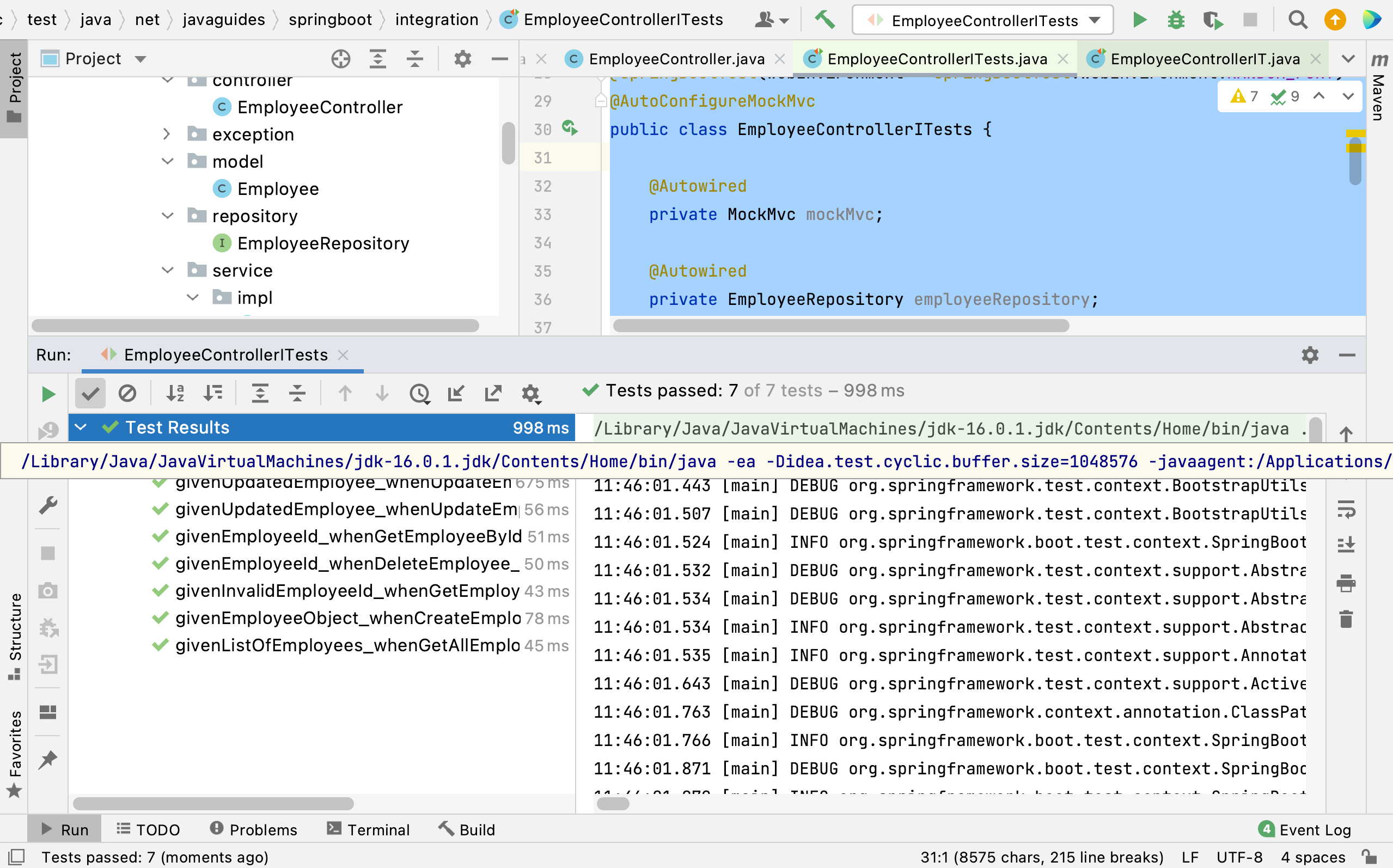
8. Demo
Here is the output of the above Integration test cases:
9. Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have discussed how to perform Spring Boot Integration testing with MySQL using @SpringBootTest annotation.