Spring Boot Project Architecture
In this article, we will discuss how to create three-layered architecture in typical Spring boot MVC projects.
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can "just run". Three-tier (or three-layer) architecture is a widely accepted solution to organize the codebase. According to this architecture, the codebase is divided into three separate layers with distinctive responsibilities.
Three Tier (Three Layer) Architecture
Spring Boot follows a layered architecture in which each layer communicates with the layer directly below or above (hierarchical structure) it:
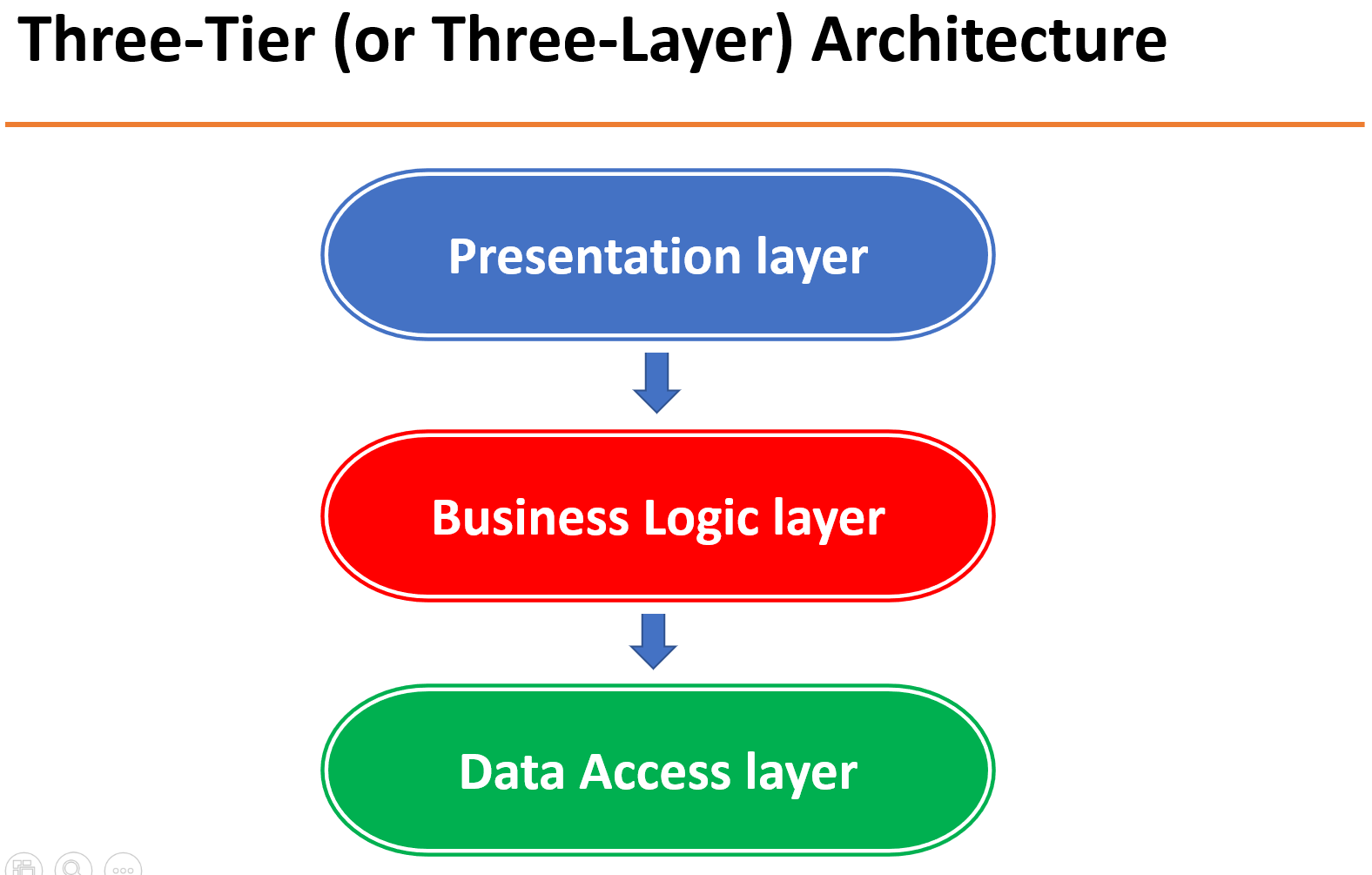
Presentation layer:This is the user interface of the application that presents the application’s features and data to the user.
Business logic (or Application) layer:This layer contains the business logic that drives the application’s core functionalities. Like making decisions, calculations, evaluations, and processing the data passing between the other two layers.
Data access layer (or Data) layer:This layer is responsible for interacting with databases to save and retrieve application data.
Spring Boot Flow Architecture ( Example)
The below diagram shows the typical application flow of our Spring boot MVC web application with Thymeleaf:
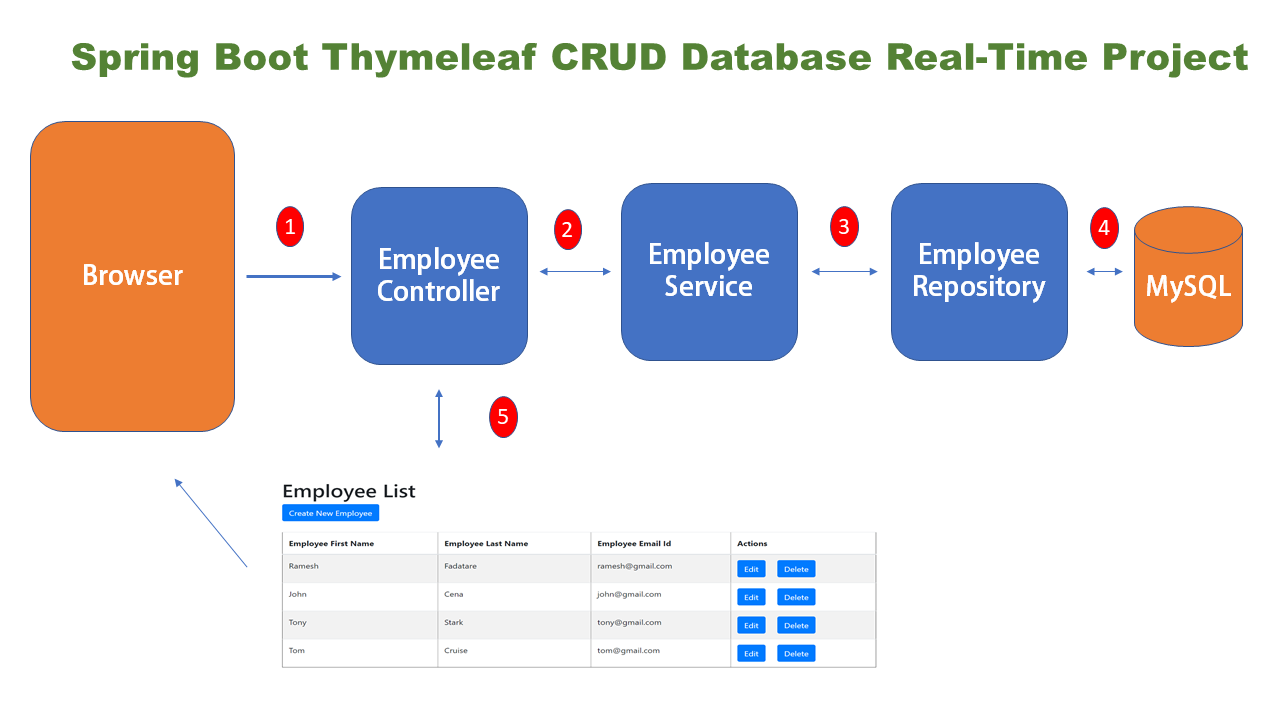
- Spring MVC controller receives an HTTP request from the client ( browser).
- Spring MVC controller process the request and sends that request to the service layer.
- Service Layer responsible to hold the business logic of the application.
- Repository layer responsible for interacting with databases to save and retrieve application data.
- Spring MVC controller return view ( JSP or Thymeleaf) to render on the browser.
Know how Spring MVC works at How Spring MVC Works Internally
How to use Three-layer architecture in Spring Boot MVC web applications.
In a Spring boot MVC web application, the three layers of the architecture will manifest as follows:
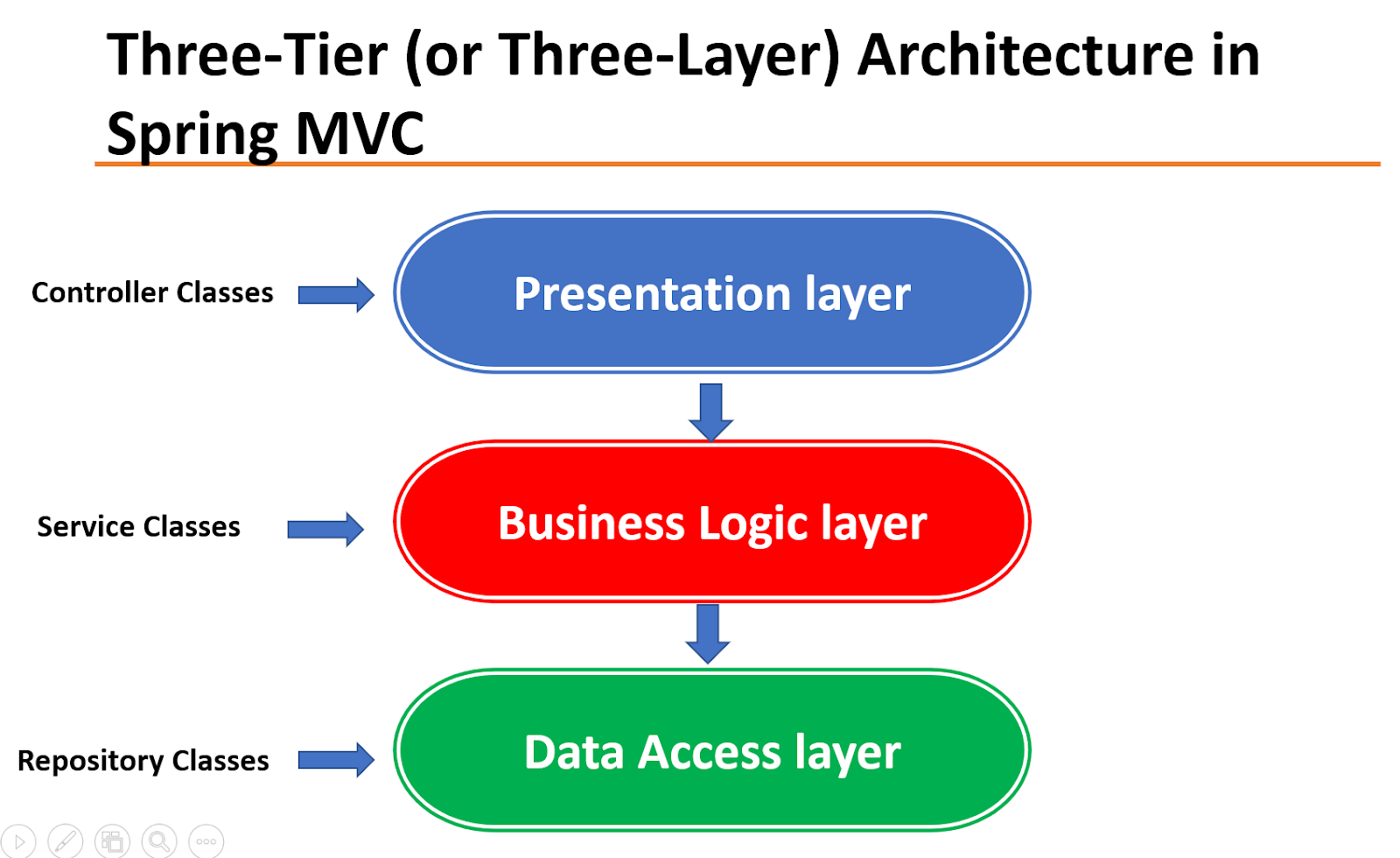
- Controller classesas the presentation layer. Keep this layer as thin as possible and limited to the mechanics of the MVC operations, e.g., receiving and validating the inputs, manipulating the model object, returning the appropriate ModelAndView object, and so on. All the business-related operations should be done in the service classes. Controller classes are usually put in a controller package.
- Service classes as the business logic layer. Calculations, data transformations, data processes, and cross-record validations (business rules) are usually done at this layer. They get called by the controller classes and might call repositories or other services. Service classes are usually put in a service package.
- Repository classesas data access layer. This layer’s responsibility is limited to Create, Retrieve, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations on a data source, which is usually a relational or non-relational database. Repository classes are usually put in a repository package.
Consider below Spring MVC web application using Spring boot and Thymeleaf. We have created a three-layer architecture and each layer is mapped to the corresponding package. For example:
- Presentation Layer -controller package
- Business Logic Layer -service package
- Data Access Layer -repository package

Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed how to create three-layered architecture in typical spring boot projects.
Three-tier (or three-layer) architecture is a widely accepted solution to organize the codebase. According to this architecture, the codebase is divided into three separate layers with distinctive responsibilities.