Spring MVC + Hibernate + JSP + MySQL CRUD Tutorial
This blog post is designed to guide you through the process of creating a CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) application using Spring MVC, Hibernate, JSP, and MySQL database.
By integrating Spring MVC with Hibernate, you can take advantage of the declarative transaction management and other powerful features provided by these frameworks. JSP (JavaServer Pages) will be used for creating dynamic and responsive views, and MySQL will handle the database operations.
Prerequisites
- Basic understanding of Java
- Familiarity with Spring MVC, Hibernate, and JSP
- MySQL installed on your system
- An Integrated Development Environment (IDE) such as Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA
1. Create a Maven Web Application
Let's create a Maven-based web application either using a command line or from Eclipse IDE.
- Use the Guide to Create a Maven Web Application link to create a Maven project using a command line.
- Use Create Maven Web Application using Eclipse IDE link to create a maven web application using IDE Eclipse.
Once you created a Maven web application, next, add the Maven dependencies.
2. Add Dependencies - pom.xml File
Open your Maven project and add the following Maven dependencies:
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>net.javaguides.springmvc</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc5-hibernate5-jsp-mysql-example</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springmvc5-hibernate5-jsp-mysql-example Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
<spring.version>5.1.0.RELEASE</spring.version>
<hibernate.version>5.3.5.Final</hibernate.version>
<hibernate.validator>5.4.1.Final</hibernate.validator>
<c3p0.version>0.9.5.2</c3p0.version>
<jstl.version>1.2.1</jstl.version>
<tld.version>1.1.2</tld.version>
<servlets.version>3.1.0</servlets.version>
<jsp.version>2.3.1</jsp.version>
<hsqldb.version>1.8.0.10</hsqldb.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring MVC Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring ORM -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hibernate Core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-core</artifactId>
<version>5.2.17.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hibernate Validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>${hibernate.validator}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSTL Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl-api</artifactId>
<version>${jstl.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>${tld.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>${servlets.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JSP Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>${jsp.version}</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
The spring-orm module provides the Spring integration with Hibernate:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
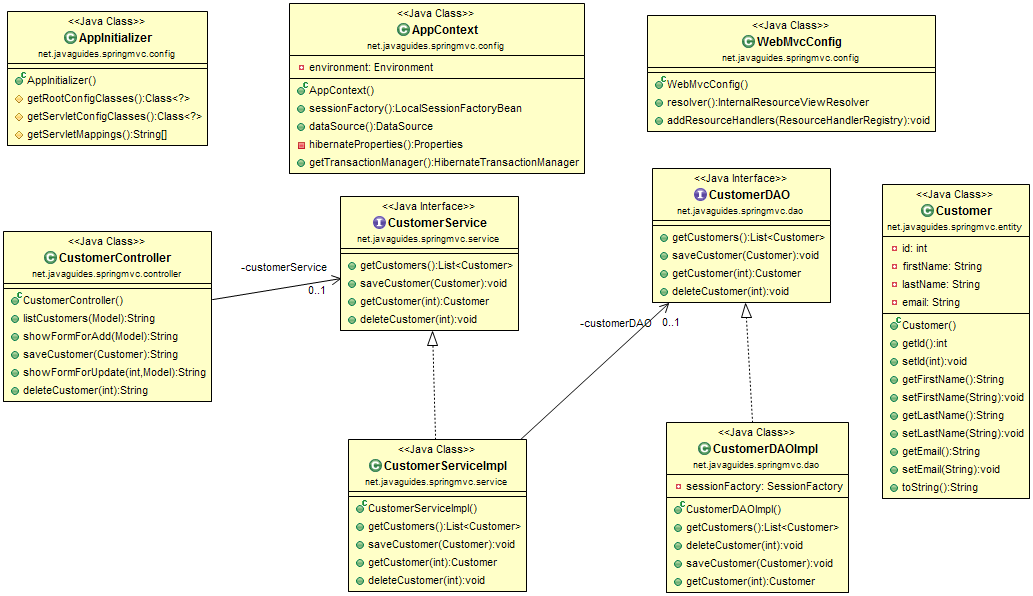
3. Create a Project Structure
Refer below screenshot to create a project structure:
Class Diagram
4. Configure DispatcherServlet using Java-based Spring configuration
In Spring MVC, The DispatcherServlet needs to be declared and mapped for processing all requests either using Java or web.xml configuration.
In a Servlet 3.0+ environment, you can use AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer class to register and initialize the DispatcherServlet programmatically as follows.
package net.javaguides.springmvc.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class AppInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class [] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] {
AppContext.class
};
//return null;
}
@Override
protected Class [] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] {
WebMvcConfig.class
};
}
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[] {
"/"
};
}
}
5. Spring and Hibernate Integration using Java-based Spring configuration
Hibernate configuration used in the example is based on hibernate Java-based configuration.
package net.javaguides.springmvc.config;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.HibernateTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.orm.hibernate5.LocalSessionFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:database.properties")
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class AppContext {
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
@Bean
public LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory() {
LocalSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new LocalSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource());
sessionFactory.setPackagesToScan(new String[] {
"net.javaguides.springmvc.entity"
});
sessionFactory.setHibernateProperties(hibernateProperties());
return sessionFactory;
}
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.driverClassName"));
dataSource.setUrl(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.url"));
dataSource.setUsername(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(environment.getRequiredProperty("jdbc.password"));
return dataSource;
}
private Properties hibernateProperties() {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("hibernate.dialect", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.dialect"));
properties.put("hibernate.show_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.show_sql"));
properties.put("hibernate.format_sql", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.format_sql"));
properties.put("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", environment.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto"));
return properties;
}
@Bean
public HibernateTransactionManager getTransactionManager() {
HibernateTransactionManager transactionManager = new HibernateTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setSessionFactory(sessionFactory().getObject());
return transactionManager;
}
}
@Configuration: Marks the class as a source of bean definitions. @PropertySource("classpath:database.properties"): Specifies the location of the database properties file in the classpath, which will be used to configure the data source and Hibernate. @EnableTransactionManagement: Enables Spring's annotation-driven transaction management.
LocalSessionFactoryBean creates a Hibernate SessionFactory. This is the usual way to set up a shared Hibernate SessionFactory in a Spring application context.
EnableTransactionManagement enables Spring’s annotation-driven transaction management capability.
HibernateTransactionManager binds a Hibernate Session from the specified factory to the thread, potentially allowing for one thread-bound Session per factory. This transaction manager is appropriate for applications that use a single Hibernate SessionFactory for transactional data access, but it also supports direct DataSource access within a transaction i.e. plain JDBC.
Create database.properties File
Create a database.properties file under the /resources folder and put the following database configuration in it.
jdbc.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useSSL=false
jdbc.username = root
jdbc.password = root
hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
hibernate.show_sql = true
hibernate.format_sql = true
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto = update
6. Spring MVC Bean Configuration using Java-based Spring configuration
Create an MVCConfig class and annotated it with @Configuration, @EnableWebMvc, and @ComponentScan annotations.
package net.javaguides.springmvc.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"net.javaguides.springmvc"
})
public class WebMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver resolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return resolver;
}
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry
.addResourceHandler("/resources/**")
.addResourceLocations("/resources/");
}
}
@Configuration: Declares that the class contains Spring Beans configuration.
@EnableWebMvc: Enables Spring's web MVC framework, allowing the use of features like @Controller and other web-related beans.
@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "net.javaguides.springmvc" }): Tells Spring to look for components (like controllers, services, repositories, etc.) inside the specified package, enabling autodetection and automatic bean registration.
InternalResourceViewResolver: This class is used to resolve the JSP views.
7. JPA Entity - Customer.java
Create the Customer class, annotate it with @Entity to map the database table, and use it for data binding with the @ModelAttribute annotation in the controller's handler method.
package net.javaguides.springmvc.entity;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name = "customer")
public class Customer {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "first_name")
private String firstName;
@Column(name = "last_name")
private String lastName;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
public Customer() {
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public void setFirstName(String firstName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Customer [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + "]";
}
}
8. Controller Layer
Let's create a Spring MVC controller called CustomerController for handling operations related to customers within an application:
package net.javaguides.springmvc.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import net.javaguides.springmvc.entity.Customer;
import net.javaguides.springmvc.service.CustomerService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/customer")
public class CustomerController {
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@GetMapping("/list")
public String listCustomers(Model theModel) {
List < Customer > theCustomers = customerService.getCustomers();
theModel.addAttribute("customers", theCustomers);
return "list-customers";
}
@GetMapping("/showForm")
public String showFormForAdd(Model theModel) {
Customer theCustomer = new Customer();
theModel.addAttribute("customer", theCustomer);
return "customer-form";
}
@PostMapping("/saveCustomer")
public String saveCustomer(@ModelAttribute("customer") Customer theCustomer) {
customerService.saveCustomer(theCustomer);
return "redirect:/customer/list";
}
@GetMapping("/updateForm")
public String showFormForUpdate(@RequestParam("customerId") int theId,
Model theModel) {
Customer theCustomer = customerService.getCustomer(theId);
theModel.addAttribute("customer", theCustomer);
return "customer-form";
}
@GetMapping("/delete")
public String deleteCustomer(@RequestParam("customerId") int theId) {
customerService.deleteCustomer(theId);
return "redirect:/customer/list";
}
}
@Controller marks the class as a Spring MVC controller.
@RequestMapping("/customer") maps all methods in this class to URLs that start with "/customer".
@Autowired injects an implementation of CustomerService, which is used to interact with the underlying data related to customers.
9. Service Layer
Let's create the CustomerService interface and its implementation and add the following content to it:
CustomerService.java
package net.javaguides.springmvc.service;
import java.util.List;
import net.javaguides.springmvc.entity.Customer;
public interface CustomerService {
public List < Customer > getCustomers();
public void saveCustomer(Customer theCustomer);
public Customer getCustomer(int theId);
public void deleteCustomer(int theId);
}
CustomerServiceImpl.java
We are using @Transactional annotation which is applied to the service layer for transaction support. @Service annotation is used to annotate service layer implementation classes as in the below file.
package net.javaguides.springmvc.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import net.javaguides.springmvc.dao.CustomerDAO;
import net.javaguides.springmvc.entity.Customer;
@Service
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
@Autowired
private CustomerDAO customerDAO;
@Override
@Transactional
public List < Customer > getCustomers() {
return customerDAO.getCustomers();
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void saveCustomer(Customer theCustomer) {
customerDAO.saveCustomer(theCustomer);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public Customer getCustomer(int theId) {
return customerDAO.getCustomer(theId);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void deleteCustomer(int theId) {
customerDAO.deleteCustomer(theId);
}
}
10. DAO Layer
Let's create the Dao layer with the CustomerDAO interface and its implementation CustomerDAOImpl class. In Spring, we annotate Dao implementation classes with @Repository annotation.
CustomerDAO.java
package net.javaguides.springmvc.dao;
import java.util.List;
import net.javaguides.springmvc.entity.Customer;
public interface CustomerDAO {
public List < Customer > getCustomers();
public void saveCustomer(Customer theCustomer);
public Customer getCustomer(int theId);
public void deleteCustomer(int theId);
}
CustomerDAOImpl.java
package net.javaguides.springmvc.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.persistence.Query;
import javax.persistence.criteria.CriteriaBuilder;
import javax.persistence.criteria.CriteriaQuery;
import javax.persistence.criteria.Root;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import net.javaguides.springmvc.entity.Customer;
@Repository
public class CustomerDAOImpl implements CustomerDAO {
@Autowired
private SessionFactory sessionFactory;
@Override
public List < Customer > getCustomers() {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
CriteriaBuilder cb = session.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery < Customer > cq = cb.createQuery(Customer.class);
Root < Customer > root = cq.from(Customer.class);
cq.select(root);
Query query = session.createQuery(cq);
return query.getResultList();
}
@Override
public void deleteCustomer(int id) {
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Customer book = session.byId(Customer.class).load(id);
session.delete(book);
}
@Override
public void saveCustomer(Customer theCustomer) {
Session currentSession = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
currentSession.saveOrUpdate(theCustomer);
}
@Override
public Customer getCustomer(int theId) {
Session currentSession = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
Customer theCustomer = currentSession.get(Customer.class, theId);
return theCustomer;
}
}
11. View Layer
customer-form.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" prefix="form"%>
<%@taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="ISO-8859-1">
<title>Spring MVC 5 - form handling | Java Guides</title>
<link href="<c:url value="/resources/css/bootstrap.min.css" />"
rel="stylesheet">
<script src="<c:url value="/resources/js/jquery-1.11.1.min.js" />"></script>
<script src="<c:url value="/resources/js/bootstrap.min.js" />"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-7">
<h2 class="text-center">Spring MVC 5 + Hibernate 5 + JSP + MySQL
Example</h2>
<div class="panel panel-info">
<div class="panel-heading">
<div class="panel-title">Add Customer</div>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<form:form action="saveCustomer" cssClass="form-horizontal"
method="post" modelAttribute="customer">
<!-- need to associate this data with customer id -->
<form:hidden path="id" />
<div class="form-group">
<label for="firstname" class="col-md-3 control-label">First
Name</label>
<div class="col-md-9">
<form:input path="firstName" cssClass="form-control" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="lastname" class="col-md-3 control-label">Last
Name</label>
<div class="col-md-9">
<form:input path="lastName" cssClass="form-control" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="email" class="col-md-3 control-label">Email</label>
<div class="col-md-9">
<form:input path="email" cssClass="form-control" />
</div>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<!-- Button -->
<div class="col-md-offset-3 col-md-9">
<form:button cssClass="btn btn-primary">Submit</form:button>
</div>
</div>
</form:form>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
list-customers.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1"
pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head><%@ page isELIgnored="false" %>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>javaguides.net</title>
<link href="<c:url value="/resources/css/bootstrap.min.css" />"
rel="stylesheet">
<script src="<c:url value="/resources/js/jquery-1.11.1.min.js" />"></script>
<script src="<c:url value="/resources/js/bootstrap.min.js" />"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="col-md-offset-1 col-md-10">
<h2>CRM - Customer Relationship Manager</h2>
<hr />
<input type="button" value="Add Customer"
onclick="window.location.href='showForm'; return false;"
class="btn btn-primary" />
<br/><br/>
<div class="panel panel-info">
<div class="panel-heading">
<div class="panel-title">Customer List</div>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<table class="table table-striped table-bordered">
<tr>
<th>First Name</th>
<th>Last Name</th>
<th>Email</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
<!-- loop over and print our customers -->
<c:forEach var="tempCustomer" items="${customers}">
<!-- construct an "update" link with customer id -->
<c:url var="updateLink" value="/customer/updateForm">
<c:param name="customerId" value="${tempCustomer.id}" />
</c:url>
<!-- construct an "delete" link with customer id -->
<c:url var="deleteLink" value="/customer/delete">
<c:param name="customerId" value="${tempCustomer.id}" />
</c:url>
<tr>
<td>${tempCustomer.firstName}</td>
<td>${tempCustomer.lastName}</td>
<td>${tempCustomer.email}</td>
<td>
<!-- display the update link --> <a href="${updateLink}">Update</a>
| <a href="${deleteLink}"
onclick="if (!(confirm('Are you sure you want to delete this customer?'))) return false">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
12. Serve Static Resources - CSS and JS
- Create a resource folder under webapp directory.
- Create css and js folders under the resource directory.
- Download and keep the bootstrap.min.css file under css folder
- download and keep bootstrap.min.js and jquery-1.11.1.min.js files under the resource directory. Note that bootstrap min js is dependent on jquery min js.
13. Build and Run an application
As we are using the maven build tool so first, we will need to build this application using the following maven command:
clean install
Once the build success, then we will run this application on Tomcat server 8.5 in IDE or we can also deploy the war file on the external Tomcat webapps folder and run the application.
Demo
Once an application is up and running in Tomcat server then hit this link into the browser: http://localhost:8080/springmvc5-hibernate5-jsp-mysql-example/customer/list
Add Customer page :
List of customers:
Conclusion
In this spring hibernate integration tutorial, we have seen how to create a Spring MVC web application and integrate it with Hibernate using Java-based configuration.