Spring Data JPA Sorting Example
In this tutorial, we will learn how to implement sorting using Spring Data JPA.
Spring Data JPA Sorting Overview
To use paging and sorting APIs provided by Spring Data JPA, your repository interface must extend the
PagingAndSortingRepository interface.
PagingAndSortingRepository is an extension of the CrudRepository to provide
additional methods to retrieve entities using the pagination and sorting abstraction. It provides two
methods :
Page findAll(Pageable pageable)– returns a Page of entities meeting the paging restriction provided in the Pageable object.Iterable findAll(Sort sort)– returns all entities sorted by the given options. No paging is applied here.
Here is the internal source code of the PagingAndSortingRepository interface:
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface PagingAndSortingRepository<T, ID> extends CrudRepository<T, ID> {
/**
* Returns all entities sorted by the given options.
*
* @param sort
* @return all entities sorted by the given options
*/
Iterable<T> findAll(Sort sort);
/**
* Returns a {@link Page} of entities meeting the paging restriction provided in the {@code Pageable} object.
*
* @param pageable
* @return a page of entities
*/
Page<T> findAll(Pageable pageable);
}
JpaRepository interface extends the PagingAndSortingRepository interface so if your
repository interface is of type JpaRepository, you don’t have to make a change to it.
For sorting, we are going to use the below method from the PagingAndSortingRepository interface:
Iterable < T > findAll(Sort sort);Note: Spring Data JPA has SimpleJPARepository class which implements
PagingAndSortingRepository interface methods so we don't have to write a code to implement
PagingAndSortingRepository interface methods.
Let's create a Spring boot project from the scratch and let's implement sorting using Spring Data JPA.
Creating Spring Boot Project
Spring Boot provides a web tool called https://start.spring.io to bootstrap an application quickly. Just go to https://start.spring.io and generate a new spring boot project.
Use the below details in the Spring boot creation:
- Project Name: spring-data-jpa-course
- Project Type: Maven
- Dependencies: Spring Data JPA, MySQL Driver, Lombok
- Package Name: net.javaguides.springboot
Maven Dependencies
Here is the complete pom.xml for your reference:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>net.javaguides</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-jpa-course</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-data-jpa-course</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Configure MySQL Database
Let's use the MySQL database to store and retrieve the data in this example and we gonna use Hibernate properties to create and drop tables.
Open application.properties and add the following configuration:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo?useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=Mysql@123
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = create-drop
Make sure that you will create a demo database before running the Spring boot application. Also, change the MySQL username and password as per your MySQL installation on your machine.
Create JPA Entity - Product.java
Let's create an entity package inside a base package "net.javaguides.springboot".
Within the entity package, create a Product class with the following content:
import lombok.*;
import org.hibernate.annotations.CreationTimestamp;
import org.hibernate.annotations.UpdateTimestamp;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Entity
@Getter
@Setter
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@ToString
@Table(
name = "products",
schema = "ecommerce",
uniqueConstraints = {
@UniqueConstraint(
name = "sku_unique",
columnNames = "stock_keeping_unit"
)
}
)
public class Product {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(
strategy = GenerationType.SEQUENCE,
generator = "product_generator"
)
@SequenceGenerator(
name = "product_generator",
sequenceName = "product_sequence_name",
allocationSize = 1
)
private Long id;
@Column(name = "stock_keeping_unit", nullable = false)
private String sku;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
private String description;
private BigDecimal price;
private boolean active;
private String imageUrl;
@CreationTimestamp
private LocalDateTime dateCreated;
@UpdateTimestamp
private LocalDateTime lastUpdated;
}
Note that we are using Lombok annotations to reduce the boilerplate code.
Create Spring Data JPA Repository
Create the ProductRepository interface:
import com.springdatajpa.springboot.entity.Product;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface ProductRepository extends JpaRepository {
}
Spring Data JPA Sorting Implementation
Write a JUnit test to implement sorting:
import com.springdatajpa.springboot.entity.Product;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
public class PaginationAndSortingTest {
@Autowired
private ProductRepository productRepository;
@Test
void sorting() {
String sortBy = "price";
String sortDir = "desc";
Sort sort = sortDir.equalsIgnoreCase(Sort.Direction.ASC.name()) ?
Sort.by(sortBy).ascending() : Sort.by(sortBy).descending();
List products = productRepository.findAll(sort);
products.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
To apply only sorting in the result set, we need to create a Sort object and pass it to the
findAll() method
Sort sort = sortDir.equalsIgnoreCase(Sort.Direction.ASC.name())?
Sort.by(sortBy).ascending(): Sort.by(sortBy).descending();
List products = productRepository.findAll(sort);
Output:
Once you run the JUnit test, you will get the below output:
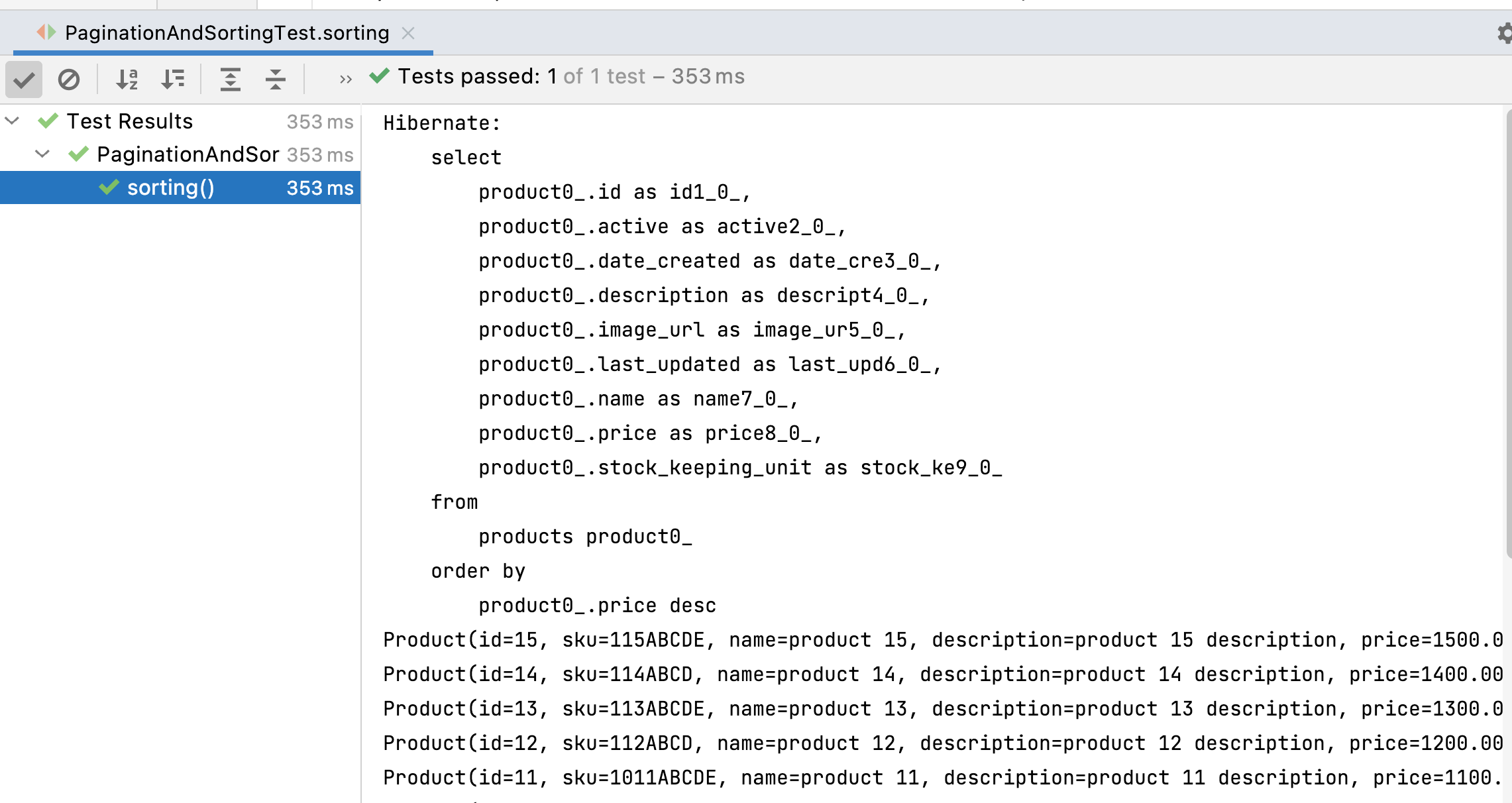
Note that Spring Data JPA behind scenes uses Hibernate to generate the below SQL query for sorting:
Spring Data JPA uses Hibernate to generate SQL queries for sorting:
select
product0_.id as id1_0_,
product0_.active as active2_0_,
product0_.date_created as date_cre3_0_,
product0_.description as descript4_0_,
product0_.image_url as image_ur5_0_,
product0_.last_updated as last_upd6_0_,
product0_.name as name7_0_,
product0_.price as price8_0_,
product0_.stock_keeping_unit as stock_ke9_0_
from
products product0_
order by
product0_.price desc