JPA EntityManager Interface with Example
EntityManager Interface Overview
A connection to a database is represented by an EntityManager instance,
which also provides functionality for
performing operations on a database. Many applications require multiple database connections during their
lifetime. For instance, in a web application, it is common to establish a separate database connection,
using a separate EntityManager instance, for every HTTP request.
An EntityManager instance is associated with a persistence context. A
persistence context is a set of entity
instances in which for any persistent entity identity there is a unique entity instance. Within the
persistence context, the entity instances and their lifecycle are managed.
The EntityManager API is used to create and remove persistent entity
instances, to find entities by their
primary key, and query over entities.
The set of entities that can be managed by a given EntityManager instance is
defined by a persistence unit.
A persistence unit defines the set of all classes that are related or grouped by the application, and which
must be colocated in their mapping to a single database.
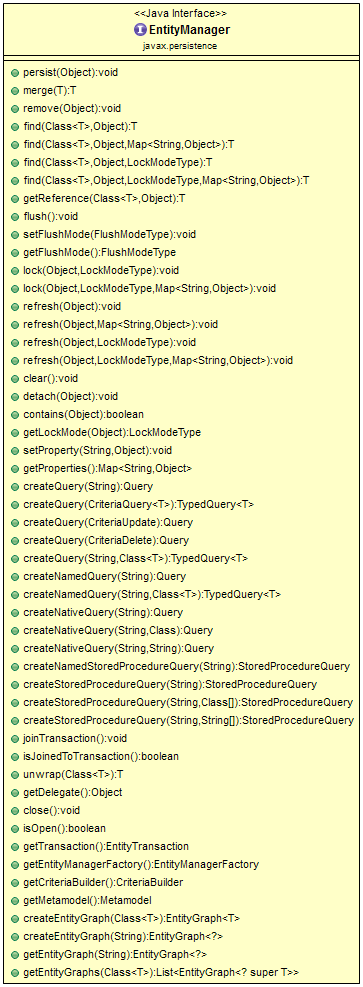
EntityManager Interface - Class Diagram
The below class diagram shows a list of methods that EntityManager Interface
provides.
EntityManager Interface Example
EntityManager Interface provides persist()
method to store an entity in a database. In this example, we will
demonstrate the usage of EntityManager Interface via persisting an entity
in a database.
Steps to persist an entity object
Step 1: Creating an entity manager factory object
The EntityManagerFactory interface is present in java.persistence
package is used to provide an entity manager.
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("PERSISTENCE");Persistence-Persistenceis a bootstrap class that is used to obtain an EntityManagerFactory interface.createEntityManagerFactory()method - The role of this method is to create and return an EntityManagerFactory for the named persistence unit. Thus, this method contains the name of the persistence unit passed in thePersistence.xmlfile.
Step 2: Obtaining an entity manager from a factory
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();EntityManager- AnEntityManageris an interfacecreateEntityManager()method - It creates new application-managedEntityManager
Step 3: Initializing an entity manager
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();getTransaction()method - This method returns the resource-level EntityTransaction object.begin()method - This method is used to start the transaction.
Step 4: Persisting data into the relational database.
entityManager.persist(student); persist()- This method is used to make an instance managed and persistent. An entity instance is passed within this method.
Step 5: Closing the transaction
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();Step 6: Releasing the factory resources
entityManager.close();
entityManagerFactory.close();
- close() - This method is used to release the factory resources.
EntityManager Interface Complete Example
private static void insertEntity() {
EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("PERSISTENCE");
EntityManager entityManager = entityManagerFactory.createEntityManager();
entityManager.getTransaction().begin();
Student student = new Student("Ramesh", "Fadatare", "rameshfadatare@javaguides.com");
entityManager.persist(student);
entityManager.getTransaction().commit();
entityManager.close();
entityManagerFactory.close();
}